Adrenal Mass
June 5, 2018 Source: Internal - karim uddin, Other Source: https://www.urologyhealth.org
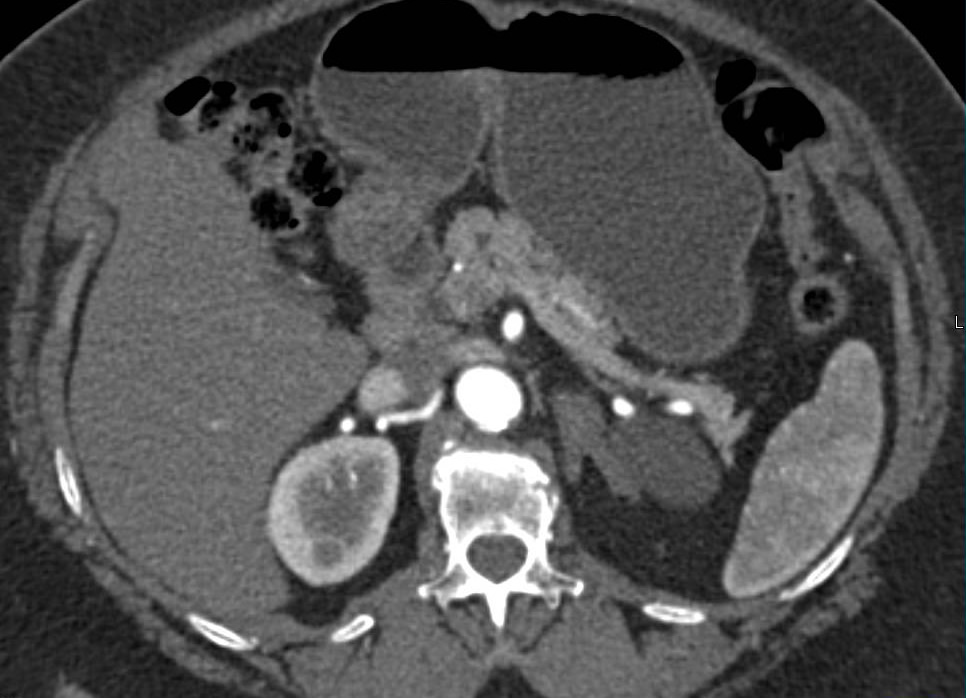
Adrenal mass is a condition where there is an irregular growth of a mass in the adrenal gland. The adrenal gland is located above each kidney and is triangular in shape. It consists of the adrenal cortex, otherwise known as the outer part, and the adrenal medulla, also known as the inner part. Both the outer and inner parts are responsible for the synthesis of specific hormones necessary for life. The adrenal cortex synthesizes hormones such as cortisone and aldosterone, and the adrenal medulla synthesizes hormones such as epinephrine. When irregular growth occurs within this gland, it interferes with the proper functioning and leads to hormonal imbalances, thus affecting everyday life.
Imbalances in levels of aldosterone, cortisone and epinephrine are disastrous as these hormones help to maintain blood pressure, salt and potassium levels and heart rate. Aldosterone is a crucial hormone needed to balance levels of sodium and potassium within the body. Too much aldosterone can lead to excess sodium retention and excess potassium secretion, thus leading to higher blood pressure. Similarly, cortisone is an anti-inflammatory hormone and aids in balancing sodium and potassium levels. Too much of cortisone can lead to imbalances in the levels of these minerals and cause swelling. The other major hormone controlled by the adrenal gland is epinephrine, which is mainly responsible for increasing both the heart rate and blood pressure. An imbalance in the levels of epinephrine can be detrimental as a constantly high heart rate and blood pressure can permanently damage blood vessels and severely damage the kidneys.
Now while these masses are benign, certain symptoms do arise when imbalances occur in hormonal levels. Some of these symptoms include high blood pressure, heart palpitations, abdominal pain, diabetes, nervousness and low potassium levels. If any of these symptoms suddenly arise, please talk to your doctor in order to correctly diagnose what the problem is, and which treatments are available. Given the size of the mass, the doctor might recommend an excision of the mass or might recommend periodic check-ups to ensure nothing serious will occur.