May 30, 2018 Source: Internal - Gleb Danylov
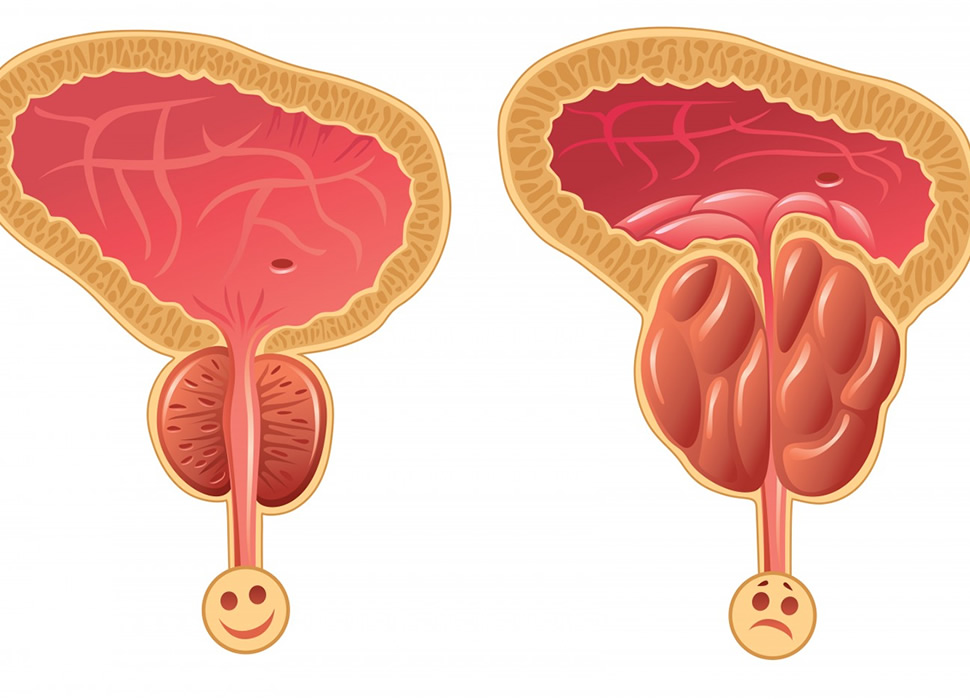
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, better known as BPH, is a condition that causes the prostate gland to enlarge. This enlargement is dangerous as an enlarged prostate can disturb the flow of urine and lead to kidney, urinary tract and bladder problems. Despite BPH being a very serious condition, it is mostly common in older men.
BPH targets the prostate gland which is located right below your bladder and is responsible for the release of urine. Overtime as age increases, the prostate gland continues to grow and can sometimes block the flow of urine, which leads to the first signs of urinary symptoms. The reason behind prostate enlargement is still unknown, but many studies suggest that it may be due to the change in the balance of sexual hormones which occur as age increases in men.
The symptoms of this condition vary with the levels of severity, but some common symptoms include the constant need to urinate, difficulty with urination, nocturia and incapability to drain the bladder. Something to be noted is that the size of the gland is not directly correlated with the severity of this condition, as a larger gland may display less severe symptoms than a smaller one.
Now while this condition mostly occurs in older men, there are certain risk factors which contribute to BPH. Some of these factors include older age, family history and other conditions such as diabetes and heart disease. As age increases past 40 years, the severity of BPH increases as half of all men experience symptoms related to this condition by age 80. In addition, having a close relative with prostate problems increases your risk of developing BPH or other urinary related problems.
If BPH is left untreated, it can lead to further complications and cause Urinary Tract Infection, Bladder Stones and damage both the kidneys and the bladder. It is very important to see a doctor if you are experiencing any urinary problems, as it may lead to more severe conditions if left untreated.